Troubleshoot a VM forward and reverse flow
Troubleshoot a VM forward and reverse flow¶
This section describes how to receive the forward and reverse flow record information of VMs from their respective vRouter compute nodes. This information helps troubleshooting communication issues between virtual machines.
The image below displays an example of communication between VM_1 and VM_2:
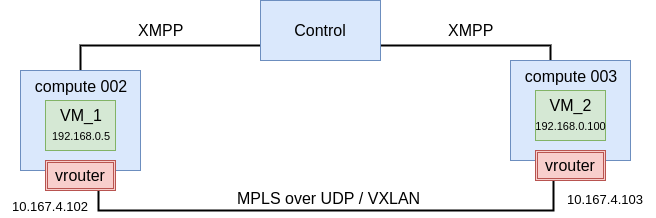
The following table shows known information about troubleshooted flows described in this section:
| Value name | VM_1 | VM_2 |
|---|---|---|
| prefix local | 192.168.0.5/32 | 192.168.0.100/32 |
| prefix remote | 192.168.0.100/32 | 192.168.0.5/32 |
To show flows between VMs:
Run the following command on one of the hosts:
For
compute 002:root@cmp002:~# flow -l | grep '192.168.0.5\|192.168.0.100'
Example of system response:
Index Source:Port/Destination:Port Proto(V) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 492152<=>1500364 192.168.0.5:792 1 (5) 192.168.0.100:0 (Gen: 1, K(nh):83, Action:F, Flags:, QOS:-1, S(nh):83, Stats:487/519142, 1500364<=>492152 192.168.0.100:792 1 (5) 192.168.0.5:0 (Gen: 1, K(nh):83, Action:F, Flags:, QOS:-1, S(nh):35, Stats:487/519142,
For
compute 003:root@cmp002:~# flow -l | grep '192.168.0.5\|192.168.0.100' # OR root@cmp002:~# flow --match "192.168.0.5,192.168.0.100"
Example of system response:
Index Source:Port/Destination:Port Proto(V) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1274292<=>1451388 192.168.0.5:792 1 (1) 192.168.0.100:0 (Gen: 15, K(nh):98, Action:F, Flags:, QOS:-1, S(nh):63, Stats:983/1047878, 1451388<=>1274292 192.168.0.100:792 1 (1) 192.168.0.5:0 (Gen: 9, K(nh):98, Action:F, Flags:, QOS:-1, S(nh):98, Stats:983/1047878,
In the output, you can see the ICMP request and response.
Pay attention to the following important parts of the output:
Action- If you get
Action: D(Sg), there might be an issue in security groups. K(nh)- It means that next hops are assigned to prefixes. It represents
nh-idfor the flow. S(nh)- This is the next hop used for RPF checks. When a flow is being setup,
agent will do route lookup for the source IP and sets up the
rpf-nhin the flow. The type of NH used depends on matched route for the source IP.
The following table describes the abbreviations used in the flow output:
| Parameter | Abbreviation description |
|---|---|
| Action |
|
| Other |
|
| Flags |
|
| TCP(r=reverse) |
|
Now, we have the following information about troubleshooted flows described in this section:
| Value name | VM_1 | VM_2 |
|---|---|---|
| prefix local | 192.168.0.5/32 | 192.168.0.100/32 |
| prefix remote | 192.168.0.100/32 | 192.168.0.5/32 |
| nh local | 83 | 98 |
| nh remote | 35 | 63 |
To get VRF ID:
Run the following commands:
For
compute 002:root@cmp002:~# nh --get 83 Id:83 Type:Encap Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:4 Vrf:5 Flags:Valid, Policy, EncapFmly:0806 Oif:8 Len:14 Encap Data: 02 29 64 b3 e2 f4 00 00 5e 00 01 00 08 00 root@cmp002:~# nh --get 35 Id:35 Type:Tunnel Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:4850 Vrf:0 Flags:Valid, MPLSoUDP, Oif:0 Len:14 Flags Valid, MPLSoUDP, Data:0c c4 7a 50 27 88 0c c4 7a 17 99 5d 08 00 Vrf:0 Sip:10.167.4.102 Dip:10.167.4.103
For
compute 003:root@cmp003:~# nh --get 98 Id:98 Type:Encap Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:5 Vrf:1 Flags:Valid, Policy, EncapFmly:0806 Oif:13 Len:14 Encap Data: 02 d1 32 42 b5 87 00 00 5e 00 01 00 08 00 root@cmp003:~# nh --get 63 Id:63 Type:Tunnel Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:20 Vrf:0 Flags:Valid, MPLSoUDP, Oif:0 Len:14 Flags Valid, MPLSoUDP, Data:0c c4 7a 17 99 5d 0c c4 7a 50 27 88 08 00 Vrf:0 Sip:10.167.4.103 Dip:10.167.4.102
Using the outputs above, we add the following information about the troubleshooted flows described in this section:
| Value name | VM_1 | VM_2 |
|---|---|---|
| prefix local | 192.168.0.5/32 | 192.168.0.100/32 |
| prefix remote | 192.168.0.100/32 | 192.168.0.5/32 |
| nh local | 83 | 98 |
| nh remote | 35 | 63 |
| VRF local | 5 | 1 |
| VRF remote | 0 | 0 |
To identify tap interface used by VMs:
Log in to an OpenStack controller node.
Identify the tap interface used by VMs:
neutron port-list | grep 192.168.0.5 | awk '{print $2}' | cut -c 1-11 | awk '{print "tap"$1}' tap2964b3e2-f4 neutron port-list | grep 192.168.0.100 | awk '{print $2}' | cut -c 1-11 | awk '{print "tap"$1}' tapd13242b5-87
You cam also get this information from the compute
cmpnode using the0ifvalue of the nh --get XY command output. For example:nh --get 83
Example of system response:
Id:83 Type:Encap Fmly: AF_INET Rid:0 Ref_cnt:4 Vrf:5 Flags:Valid, Policy, EncapFmly:0806 Oif:8 Len:14 Encap Data: 02 29 64 b3 e2 f4 00 00 5e 00 01 00 08 00
vif --get 8
Example of system response:
Vrouter Interface Table Flags: P=Policy, X=Cross Connect, S=Service Chain, Mr=Receive Mirror Mt=Transmit Mirror, Tc=Transmit Checksum Offload, L3=Layer 3, L2=Layer 2 D=DHCP, Vp=Vhost Physical, Pr=Promiscuous, Vnt=Native Vlan Tagged Mnp=No MAC Proxy, Dpdk=DPDK PMD Interface, Rfl=Receive Filtering Offload, Mon=Interface is Monitored Uuf=Unknown Unicast Flood, Vof=VLAN insert/strip offload, Df=Drop New Flows, Proxy=MAC Requests Proxied Always vif0/8 OS: tap2964b3e2-f4 Type:Virtual HWaddr:00:00:5e:00:01:00 IPaddr:0 Vrf:5 Flags:PL3L2D QOS:-1 Ref:5 RX packets:7221 bytes:5897180 errors:0 TX packets:7229 bytes:6023816 errors:0 Drops:15
You can compare the
Vrfparameter of this output with the output forId:83.
Using the outputs above, we add the following information about the troubleshooted flows described in this section:
| Value name | VM_1 | VM_2 |
|---|---|---|
| prefix local | 192.168.0.5/32 | 192.168.0.100/32 |
| prefix remote | 192.168.0.100/32 | 192.168.0.5/32 |
| nh local | 83 | 98 |
| nh remote | 35 | 63 |
| VRF local | 5 | 1 |
| VRF remote | 0 | 0 |
| Tap Interface | tap2964b3e2-f4 | tapd13242b5-87 |
To verify a routing table for VRF (routing instance):
Show or dump the routing table of the required VRF using the rt command
For
compute 002:root@cmp002:~# rt --dump 5 | grep 192.168.0.5/32 192.168.0.5/32 32 P - 83 2:29:64:b3:e2:f4(240568) root@cmp002:~# rt --dump 5 | grep 192.168.0.100/32 192.168.0.100/32 32 LP 44 35 2:d1:32:42:b5:87(149684)
For
compute 003:root@cmp003:~# rt --dump 1 | grep 192.168.0.5/32 192.168.0.5/32 32 LP 33 63 2:29:64:b3:e2:f4(159964) root@cmp003:~# rt --dump 1 | grep 192.168.0.100/32 192.168.0.100/32 32 P - 98 2:d1:32:42:b5:87(227736)
If the above procedure does not resolve the issues, proceed with the following steps:
- Verify that a network policy is created.
- Verify that a network policy is assigned to VMs.
- Verify the rules of a security group.
- Verify that virtual networks (VNs) are assigned a correct security group.
- Verify that the routing table using the rt --dump <VRF_ID> if prefixes were exchanged.
- Verify MTU on physical interface used by vRouter.
- Verify the MTU jumbo frames in the underlay network.