Mirantis Container Cloud (MCC) becomes part of Mirantis OpenStack for Kubernetes (MOSK)!
Starting with MOSK 25.2, the MOSK documentation set covers all product layers, including MOSK management (formerly Container Cloud). This means everything you need is in one place. Some legacy names may remain in the code and documentation and will be updated in future releases. The separate Container Cloud documentation site will be retired, so please update your bookmarks for continued easy access to the latest content.
Cluster types¶
The types of Mirantis OpenStack for Kubernetes (MOSK) clusters include:
- Bootstrap cluster
Runs the bootstrap process on a seed data center bare metal node.
Requires access to the bare metal provider backend.
Initially, the bootstrap cluster is created with the following minimal set of components: Bootstrap Controller, public API charts, and the Bootstrap API.
The user can interact with the bootstrap cluster through the Bootstrap API to create the configuration for a management cluster and start its deployment. More specifically, the user performs the following operations:
Create required deployment objects.
Optionally add proxy and SSH keys.
Configure the cluster and machines.
Deploy the management cluster.
The user can monitor the deployment progress of the cluster and machines.
After a successful deployment, the user can download the
kubeconfigartifact of the provisioned cluster.
- Management cluster
Provides the following functionality:
Runs all public APIs and services including the management console of the MOSK management cluster.
Runs the baremetal-specific services and internal API including
LCMMachineandLCMCluster. Also, it runs an LCM controller for orchestrating MOSK clusters and other controllers for handling different resources.Requires two-way access to the bare metal provider backend. The provider connects to a backend to spawn MOSK cluster nodes, and the agent running on the nodes accesses the management cluster to obtain the deployment information.
For deployment details of a management cluster, see Deploy a management cluster.
- MOSK cluster
A Mirantis Kubernetes Engine (MKE) cluster that an end user creates using the management console.
Requires access to its management cluster. Each node of a MOSK cluster runs an LCM Agent that connects to the LCM machine of the management cluster to obtain the deployment details.
Combines OpenStack, an open-source cloud infrastructure software, with application management techniques used in the Kubernetes ecosystem
All types of MOSK clusters except the bootstrap cluster are based on the MKE and Mirantis Container Runtime (MCR) architecture. For details, see MKE and MCR documentation.
The following diagram illustrates the distribution of services between each type of MOSK clusters:
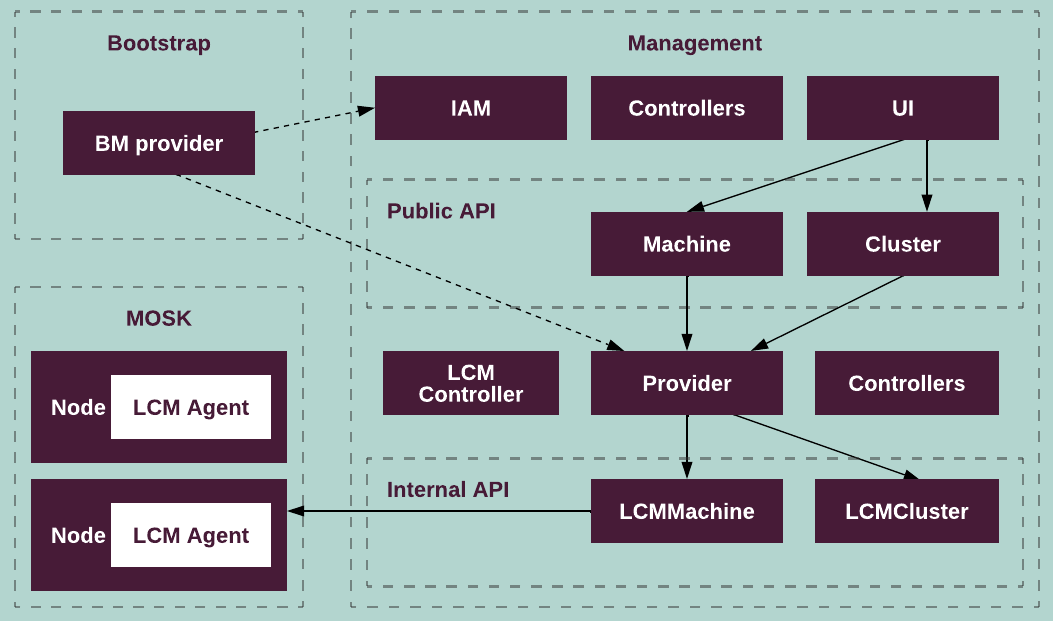
All artifacts used by Kubernetes and workloads are stored on the Mirantis content delivery network (CDN):
mirror.mirantis.com(Debian packages including the Ubuntu mirrors)binary.mirantis.com(Helm charts and binary artifacts)mirantis.azurecr.io(Docker image registry)
All MOSK components are deployed in the Kubernetes clusters. All MOSK management APIs are implemented using the Kubernetes Custom Resource Definition (CRD) that represents custom objects stored in Kubernetes and allows you to expand Kubernetes API.
The MOSK logic is implemented using controllers. A
controller handles changes in custom resources defined in the controller CRD.
A custom resource consists of a spec that describes the desired state of a
resource provided by the user. During every change, a controller reconciles
the external state of a custom resource with the user parameters and stores
this external state in the status subresource of its custom resource.